Articles
The Role of Breathwork in Athletic Performance: Increasing Endurance & Strength
Contents Overview
Table of Contents
In recent years, breathwork has emerged as a powerful addition to athletic training programs worldwide. From elite marathon runners to powerlifters, athletes are tapping into specific breathing techniques to boost strength, stamina, focus, and mental resilience. Breathwork goes beyond basic breathing exercises; it’s a structured practice that optimizes oxygen use, balances the nervous system, and enhances physical endurance, making it an essential tool for achieving peak performance. The Breatheology Method, created by world-renowned freediver Stig Severinsen, provides a unique, science-backed approach that combines ancient techniques with modern sports insights to take athletic performance to new levels.
Why Breathwork Matters for Athletes: Overview
Athletic success relies on how efficiently the body uses oxygen and manages stress. During intense physical activity, muscles need substantial oxygen to produce energy and sustain performance. Controlled breathing exercises improve the body’s ability to use oxygen effectively and regulate cardiovascular function, which helps athletes perform with less fatigue. Breathwork also influences mental clarity and resilience, helping athletes stay focused, calm, and composed in competitive situations.
Studies and firsthand accounts from top athletes highlight how breathwork can:
- Enhance muscular endurance by optimizing oxygen flow.
- Improve breath efficiency, supporting prolonged activity without premature exhaustion.
- Reduce stress and anxiety, fostering calmness and clarity during high-pressure events.
Integrating breathwork into a training routine fine-tunes both the mental and physical aspects of performance, making it a valuable resource for athletes at all levels.
The Science Behind Breathwork in Athletic Performance

Breathwork engages several physiological systems that are crucial for athletic efficiency and resilience. Understanding how these systems work helps clarify why breathwork has such a profound effect on athletic performance.
Oxygen Efficiency and Energy Production
The body’s demand for oxygen increases during exercise, especially for endurance athletes. In high-intensity activities, the body may shift toward anaerobic energy systems, producing lactic acid, which can lead to muscle fatigue. Breathwork improves oxygen efficiency, allowing the lungs to absorb and deliver oxygen more effectively. This supports higher energy levels over extended periods and reduces muscle fatigue.
Cardiovascular Regulation
Breathwork helps regulate heart rate and blood flow, particularly during endurance activities, by activating the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). Techniques like resonant breathing and box breathing stabilize the heart rate, allowing athletes to maintain a steady pace without burning out quickly. Consistent practice of these techniques also aids recovery by restoring a calm heart rate post-exertion.
Nervous System and Stress Management
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), which includes the sympathetic (fight-or-flight) and parasympathetic (rest-and-digest) branches, plays a key role in handling stress and focus. Breathwork activates the parasympathetic system to calm the body, reduce anxiety, and increase focus. This calm state is crucial for high-pressure scenarios where athletes need to make quick, precise decisions. Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing and box breathing are effective for calming the nervous system, allowing athletes to perform at their best even under intense pressure.
Training the Lungs for Peak Performance
Our lungs serve as the “fuel tank” of the body, and breath training helps athletes maximize this capacity. As the Breatheology Method highlights, breath training increases the lungs’ ability to absorb and efficiently distribute oxygen, similar to fueling a high-performance vehicle. By refining how the lungs operate, athletes enhance their oxygen intake, maintain stamina, and support faster recovery.
Improved Mental Control Under Pressure
An athlete’s ability to keep calm and focused under pressure is invaluable. Breathwork helps athletes remain mentally composed, which is essential for maintaining precision and confidence in competition. Techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing enable athletes to manage stress responses by controlling their breath, helping them keep their mind clear in high-stakes moments.
Breathwork Techniques for Stress Management in Athletic Performance
For athletes, managing stress is essential for consistent peak performance. Breathwork not only enhances physical endurance but is also highly effective for reducing anxiety, promoting calm, and enhancing mental resilience. These breathwork techniques are beneficial before competitions to ease nerves, during performance to maintain focus, and afterward for recovery.
1. Diaphragmatic Breathing for Instant Calm
Diaphragmatic breathing, or “belly breathing,” promotes relaxation by focusing on deep, slow breathing from the diaphragm. This technique activates the parasympathetic nervous system, lowering heart rate and stabilizing blood pressure. It’s ideal for athletes who experience pre-competition nerves or who need a grounding exercise after intense physical exertion.
- How to Practice: Sit comfortably or lie down, placing one hand on the chest and the other on the abdomen. Breathe in deeply through your nose, allowing your abdomen to expand, and exhale slowly through your mouth. Repeat for several minutes, focusing on the rhythm.
- Benefits: Reduces anxiety, lowers heart rate, and promotes a calm yet alert state.
2. Box Breathing for Mental Resilience
Box breathing is a structured method where inhaling, holding, exhaling, and holding the breath are done for equal counts. This technique helps the body adapt to stress by balancing the nervous system and is particularly popular in high-stress environments, such as military training.
- How to Practice: Inhale for a count of 4, hold the breath for 4, exhale for 4, and hold again for 4. Repeat this cycle several times.
- Benefits: Balances the nervous system, sharpens focus, and supports rapid recovery from intense physical or mental exertion.
3. Resonant Breathing for Reduced Tension
Resonant breathing, also known as coherent breathing, is performed at a rate of around six breaths per minute. This technique synchronizes heart rate with breathing patterns, promoting a relaxed but focused state. It’s ideal for athletes during recovery periods or after high-stress events.
- How to Practice: Inhale for a count of 5 and exhale for a count of 5, keeping a steady rhythm. Continue for five to ten minutes.
- Benefits: Calms the nervous system, enhances cardiovascular efficiency, and reduces physical and mental tension.
How Breathwork Enhances Endurance in Long-Distance Sports

For endurance athletes like runners, cyclists, and swimmers, breathwork helps in sustaining energy over prolonged activities. Improved oxygen efficiency from techniques like diaphragmatic and resonant breathing allows athletes to train and compete at higher intensities with less exhaustion.
Example: Long-Distance Running
In long-distance running, steady and controlled breathing helps runners manage a consistent heart rate and rhythm. Diaphragmatic breathing, for example, helps runners avoid shallow breathing, which can lead to early fatigue. This technique enhances lung efficiency, helping athletes maintain their pace without overworking their muscles.
Example: Competitive Swimming
Swimmers face unique challenges in coordinating breath with stroke timing, especially in high-intensity events. Techniques like breath-holding and controlled exhales improve lung control, allowing swimmers to minimize breathing frequency and focus on stroke efficiency. Breath-Hold Masterclass offers advanced breath-hold techniques that help to build CO₂ tolerance and adapt to oxygen-limited environments.
Strength and Power: Breathwork for Anaerobic Sports

In anaerobic sports that require short, explosive power, breath-holding exercises can be beneficial. Breath-hold practices help train the body to function in low-oxygen conditions, supporting powerlifters, sprinters, and gymnasts in building strength, core stability, and explosiveness.
Example: Powerlifting and the Valsalva Maneuver
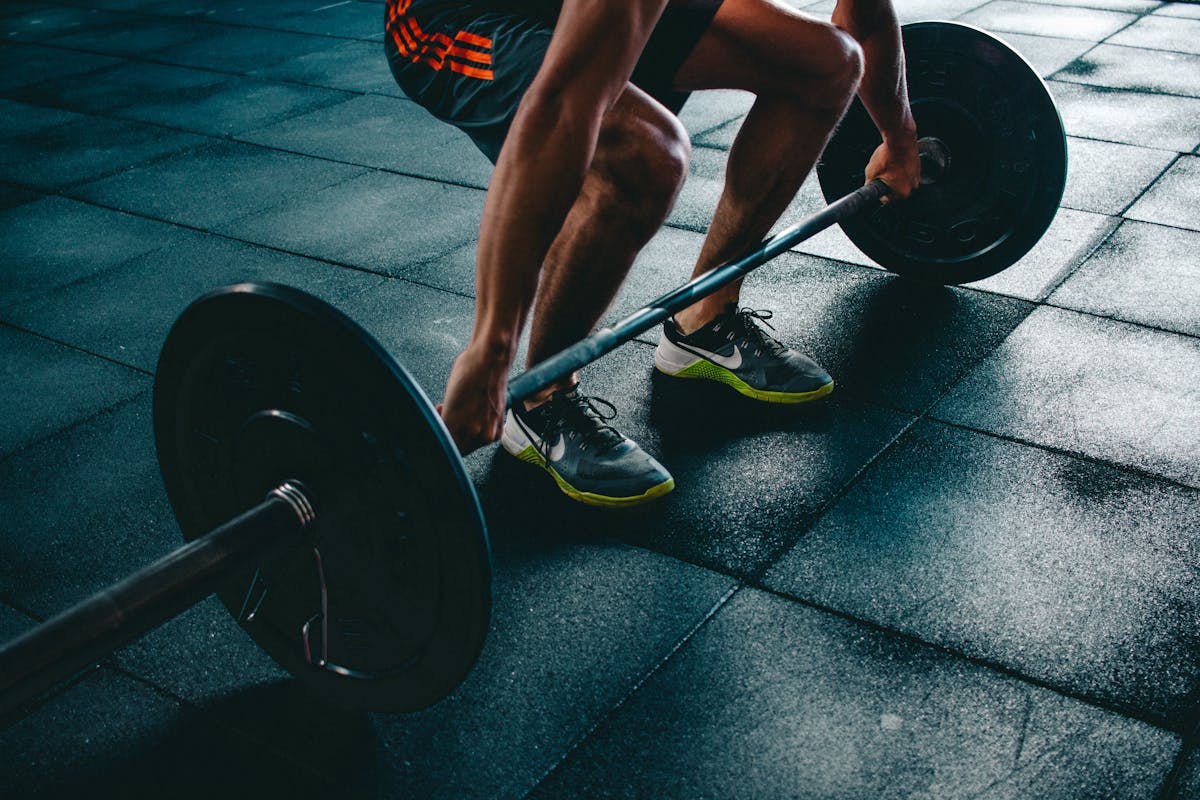

Powerlifters often use the Valsalva maneuver, a technique involving breath-holding during heavy lifts to increase core stability. By creating intra-abdominal pressure, the Valsalva maneuver helps lifters maintain balance and strength. However, proper technique and guidance are essential, as this method temporarily increases blood pressure.
Famous Athletes Who Use Breathwork to Enhance Performance
Many elite athletes recognize the power of breathwork in boosting endurance, mental clarity, and resilience:
- Laird Hamilton: The big-wave surfer uses breath-holding techniques to stay calm in intense surf conditions, enabling him to navigate massive waves safely.
- Novak Djokovic: The tennis champion practices yoga and breathwork to manage stress and maintain focus during intense tournaments.
- LeBron James: LeBron incorporates breathwork into his recovery routines, helping him sustain peak performance over long basketball seasons.
- Conor McGregor: Known for his rigorous training, McGregor uses the Wim Hof Method to build mental toughness and pain tolerance, essential traits for MMA.
Conclusion
Breathwork offers athletes a versatile way to improve both physical and mental performance. From enhancing endurance to building mental resilience, integrating breathwork into training routines offers valuable support for peak athletic achievement. For athletes new to breathwork, starting with five to ten minutes of basic breathing exercises each day can yield significant benefits.
Breatheology Courses
Learn and master conscious breathing through our online breathwork courses. Discover how simple yet powerful breathing techniques can help reduce stress, improve your mental clarity, and boost your physical performance.
Free Breathwork Courses
Kickstart your breath training journey with our free, step-by-step breathing programs designed to help you improve lung capacity, manage stress, and build focus.
Advanced Breathwork Training
Take your breathing mastery to the next level with our advanced breathwork training programs. Build resilience, enhance your endurance, and unlock greater physical and mental performance.
Similar Posts:
- How to Improve Breathing: A Complete Guide
- A comprehensive guide on breathing techniques to enhance athletic performance.
- Energizing Breath and Its Benefits for Physical Vitality
- Breathing strategies that boost energy and improve physical vitality for athletes.
- The Science of Breathing and the Nervous System
- Explores how breathing affects the nervous system, critical for performance under pressure.
- Understanding Heart Rate Variability (HRV) and Its Link to Emotional Resilience
- Discusses HRV, a key indicator of recovery and resilience, improved through breathwork.
References: Sports Performance and Breathing Rate: What Is the Connection
