Articles, Health & Rehabilitation, Science & Studies
How Breathing Affects Mental Health: The Science Behind Calm
Contents Overview
Table of Contents
In a world increasingly filled with stress and fast-paced demands, managing mental health is essential. Among various natural methods, breathing exercises have emerged as an effective way to address mental health challenges, including anxiety, depression, and chronic stress. Controlled breathing, which anyone can practice, works by influencing the nervous system and shifting the body into a relaxed state. In this article, we’ll explore the science behind how breathing affects mental health and discuss specific breathing techniques to promote calm and well-being.

The Link Between Breathing and Mental Health
Breathing, though often automatic, has a profound effect on mental health when used consciously. Unlike other involuntary processes, breathing is unique because it can be voluntarily controlled, creating a powerful bridge between body and mind. Learn more about how breathing influences relaxation and alertness in the nervous system.
When under stress, the body’s sympathetic nervous system (SNS) becomes activated, increasing heart rate, breathing rate, and releasing cortisol, a stress hormone. Practicing intentional, slower breathing can activate the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), responsible for calming the body and promoting relaxation. Engaging the PNS through breathing can lead to:
- Reduced levels of cortisol, leading to decreased stress and tension.
- Improved oxygen flow to the brain, enhancing clarity and concentration.
- Increased levels of GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), a calming neurotransmitter that alleviates anxiety.
These effects provide a natural means to manage daily stress and support mental resilience.
Key Mental Health Benefits of Breathing Exercises
1. Reducing Stress by Activating the Parasympathetic Nervous System
Stress causes a cascade of reactions in the body, including an increased heart rate, tense muscles, and rapid, shallow breathing. Over time, chronic stress can contribute to anxiety, irritability, and depression. Slow, deep breathing exercises help engage the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), which counters the stress response by slowing heart rate, lowering blood pressure, and reducing cortisol production. Improving Heart Rate Variability (HRV) is another benefit of these exercises, supporting emotional resilience and better stress management.
A simple and effective breathing technique for stress relief is diaphragmatic breathing, also known as belly breathing, which focuses on slow, deep breaths that expand the diaphragm. This sends a message to the brain to relax, creating an immediate sense of calm.
- How to Practice Diaphragmatic Breathing: Sit or lie down comfortably, placing one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen. Breathe in deeply through your nose, allowing your abdomen to rise while keeping your chest still. Exhale slowly through your mouth. Practice for a few minutes to experience a sense of relaxation.
- Benefits: Lowers cortisol levels, decreases heart rate, and helps the body shift into a state of calm, making it highly effective for managing daily stress.
2. Managing Anxiety with Box Breathing
Anxiety can feel overwhelming, often manifesting as racing thoughts, restlessness, and a lack of concentration. Box breathing, also called 4-4-4-4 breathing, is a structured technique that promotes a calm, focused state by regulating breathing patterns. This technique involves a rhythmic cycle of inhaling, holding the breath, exhaling, and holding again, each for four counts.
Box breathing has been shown to increase alpha brainwave activity, which supports relaxation and mental focus. By slowing the breath and enhancing concentration, box breathing can provide immediate relief from anxiety.
- How to Practice Box Breathing: Inhale slowly for a count of 4, hold the breath for a count of 4, exhale for a count of 4, and hold again for 4. Repeat this cycle for several minutes.
- Benefits: Reduces heart rate, improves focus, and alleviates anxiety, making it useful both for daily management and during high-stress moments.
3. Lifting Mood and Reducing Depression with Coherent Breathing
Coherent breathing, or resonant breathing, is practiced by breathing at a steady rate of about six breaths per minute. Research indicates that coherent breathing can increase Heart Rate Variability (HRV), which enhances the body’s ability to handle stress and improves overall emotional resilience.
Depression is often linked to a low HRV, which can make the body less adaptable to stressors. Coherent breathing helps increase HRV, supporting a more balanced and stable emotional state, even in challenging situations.
- How to Practice Coherent Breathing: Inhale for a count of 5 and exhale for a count of 5, maintaining a steady rhythm for five to ten minutes.
- Benefits: Increases HRV, reduces depressive symptoms, and helps stabilize mood by promoting a balanced nervous system response.
4. Breathing Techniques for Managing Social Anxiety and Boosting Confidence
Social anxiety can lead to uncomfortable physical symptoms like a racing heart, shallow breathing, and sweating, making social interactions feel overwhelming. Breathing exercises offer an effective way to manage these symptoms by calming the nervous system, reducing stress responses, and fostering a sense of control. With regular practice, breathwork can help alleviate the physical signs of social anxiety, promote calm, and increase confidence in social settings.
How Breathing Eases Social Anxiety and Supports Confidence
Practiced before or during social situations, controlled breathing helps lower heart rate, reduce muscle tension, and provide mental clarity, allowing individuals to feel more at ease. This boost in self-awareness and calmness makes it easier to approach social interactions confidently. Regular breathing exercises can also enhance mindfulness, making individuals more present and less self-conscious.
Recommended Breathing Techniques
- The Breatheology Method: for Social Anxiety Relief: The Breatheology Method, combines slow, controlled breathing with breath-holding exercises to help build tolerance to stress and reduce anxiety. This method can be particularly useful in managing social anxiety by calming the nervous system and promoting mental clarity.
- How to Practice: Start by taking a few deep, slow breaths through the nose, focusing on a steady rhythm. Inhale deeply, then hold your breath for a few seconds (as long as comfortable), before exhaling slowly. Repeat for several cycles, gradually extending the breath-hold time with practice.
- Power Breathing for Confidence: Power breathing involves taking slow, deep breaths with a focus on grounding oneself and creating a sense of calm strength. It is ideal for situations that require self-assurance, such as public speaking or entering a social event.
- How to Practice: Stand or sit with a straight back. Inhale deeply through your nose, filling your lungs completely, and exhale slowly through your mouth. Repeat for 1–2 minutes, focusing on cultivating a sense of empowerment and calm.
Benefits of These Techniques for Social Situations
- Calmness Under Pressure: Both Power Breathing and the Breatheology Method help reduce the physical signs of social anxiety, such as a racing heart and shallow breathing, allowing you to stay composed.
- Enhanced Self-Awareness: These breathing techniques increase mindfulness, helping you remain present in social situations and connect with others more easily.
- Increased Confidence: By calming both body and mind, breathing exercises create a sense of inner control, boosting self-confidence in social interactions.
Incorporating these techniques into your daily routine can help make social situations feel more manageable, building your confidence over time.
The Science Behind Calming Breathing Techniques
Understanding the mechanisms behind breathing exercises highlights why they’re so effective for mental health.
Impact on the Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve, a critical component of the parasympathetic nervous system, plays a significant role in managing stress and regulating mood. It runs from the brainstem to the abdomen, influencing several key organs along the way. Learn more about the role of the vagus nerve in managing stress. Certain breathing exercises can stimulate the vagus nerve, sending signals to the brain to relax and reduce anxiety, which leads to an overall feeling of calm. Techniques such as alternate nostril breathing and diaphragmatic breathing help enhance vagal tone, making the body more resilient to stress.
Balancing Neurotransmitters
Breathing exercises influence neurotransmitter levels, including serotonin and GABA. GABA is particularly important for mental health, as it has a calming effect on the brain, helping counteract excitatory neurotransmitters that are linked with anxiety. Slow, rhythmic breathing has been shown to increase GABA levels naturally, which can improve mood and decrease stress. Read more on Neurotransmitters and Breathing: Balancing Serotonin, GABA, and Dopamine
Regulating Cortisol Production
Cortisol, known as the body’s primary stress hormone, is released during times of stress. Chronic high levels of cortisol are linked with anxiety, depression, and physical health issues. By promoting the parasympathetic nervous system, breathing exercises help reduce cortisol production, enabling the body to relax and recover from stress.
Effective Breathing Techniques for Mental Health
Here are several breathing exercises proven to support mental health by reducing stress, anxiety, and symptoms of depression.
1. Diaphragmatic Breathing for Relaxation
Diaphragmatic breathing, or belly breathing, is effective in quickly calming the nervous system. It’s often the foundation of many breathing techniques due to its simplicity and impact.
- How to Practice: Sit comfortably with one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen. Inhale deeply through your nose, expanding your diaphragm rather than your chest. Exhale slowly through your mouth, repeating this rhythm for several minutes.
- Benefits: Reduces cortisol levels, decreases heart rate, and brings the body into a relaxed state, ideal for managing daily stress or immediate anxiety.
2. Alternate Nostril Breathing for Balancing Emotions
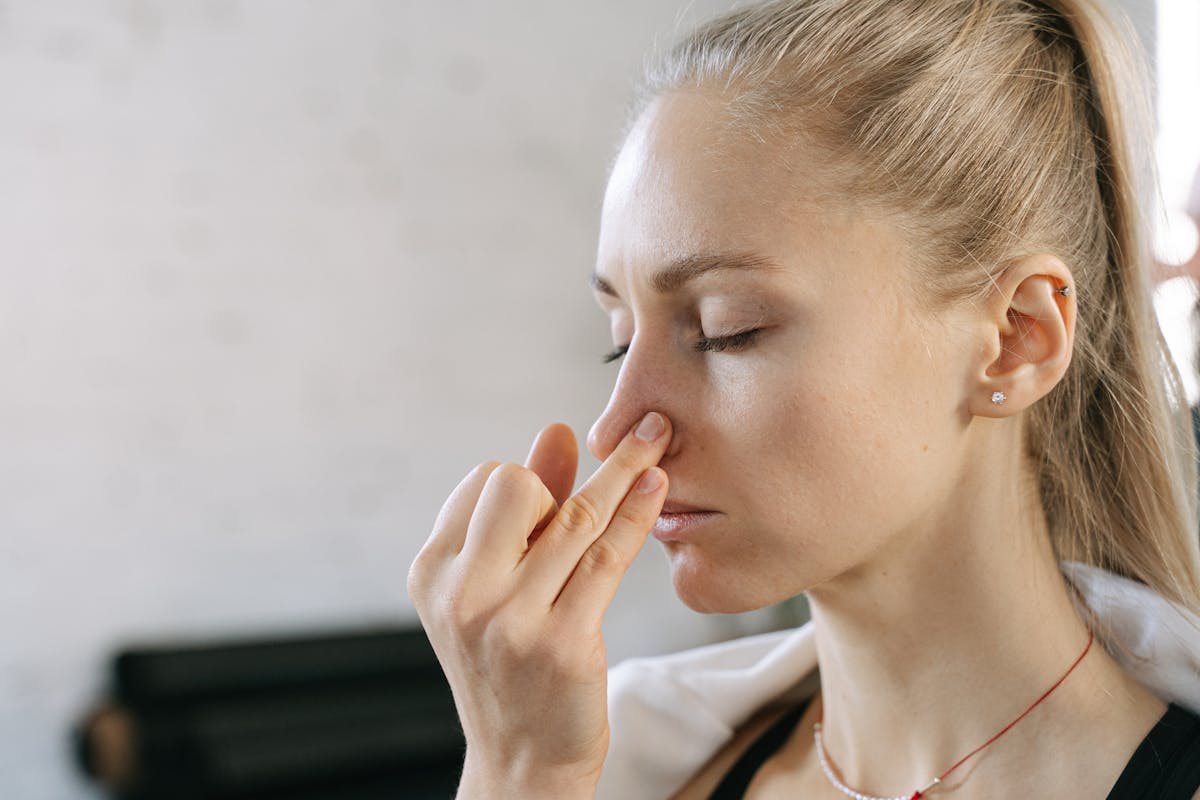

Alternate nostril breathing, also called Nadi Shodhana, involves breathing in and out through one nostril at a time, which can help balance the left and right hemispheres of the brain. This balance promotes mental clarity and stabilizes mood, helping to alleviate anxiety.
- How to Practice: Close your right nostril with your thumb and inhale deeply through your left nostril. Close the left nostril, open the right, and exhale through the right. Inhale through the right nostril, close it, and exhale through the left. Repeat this pattern for several minutes.
- Benefits: Balances brain activity, reduces anxiety, and improves focus, making it useful for both everyday stress and moments requiring mental clarity.
3. Coherent Breathing for Emotional Stability
Coherent breathing is performed by breathing in a steady, rhythmic pattern of about six breaths per minute. This technique has been shown to stabilize mood and improve resilience to stress, making it beneficial for those experiencing symptoms of depression.
- How to Practice: Inhale for 5 seconds, exhale for 5 seconds, and continue this rhythm for five to ten minutes.
- Benefits: Increases HRV, reduces depressive symptoms, and stabilizes mood by promoting balance within the autonomic nervous system.
4. Box Breathing for Immediate Calm
Box breathing is a structured, rhythmic breathing technique that regulates the breath in four equal parts, promoting immediate relaxation and focus. This technique is often used in high-stress environments due to its simplicity and effectiveness in calming the mind.
- How to Practice: Inhale for 4 counts, hold for 4 counts, exhale for 4 counts, and hold again for 4 counts. Repeat this cycle several times.
- Benefits: Reduces anxiety, sharpens mental focus, and provides a quick reset during stressful situations.
5. Resonant Breathing for Relaxation and Mood
Resonant breathing, often practiced as six breaths per minute, creates a gentle rhythm that synchronizes with the heart rate and calms the nervous system. This technique is effective for reducing both anxiety and depressive symptoms, helping the mind to remain balanced and resilient.
- How to Practice: Inhale and exhale each for a count of 5, keeping a steady rhythm for five to ten minutes.
- Benefits: Lowers stress, reduces symptoms of depression, and promotes a stable mental state by harmonizing breathing with heart rate.
Breathing for Physical Energy and Vitality

Breathing exercises not only improve mental health but also boost physical energy and overall vitality. Controlled, deep breathing enhances oxygen delivery to the body, which fuels cells and promotes efficient bodily functions. This increase in oxygen circulation can lead to higher energy levels, better stamina, and improved physical wellness.
How Breathing Boosts Physical Energy
By increasing oxygen flow through specific techniques like diaphragmatic breathing and resonant breathing, the body’s cells receive more fuel, helping to reduce fatigue and boost physical performance. For those who struggle with energy dips or chronic fatigue, these breathing exercises can offer a natural, accessible solution to feeling more energized and physically resilient.
Breathing Techniques for Boosting Energy
- Energizing Breath (Bellows Breathing): This technique involves rapid, rhythmic breathing to invigorate the body and stimulate the sympathetic nervous system. [Learn more about Energizing Breath and its benefits for physical vitality]
- Diaphragmatic Breathing: Expands lung capacity and improves oxygen intake, which can reduce physical fatigue.
Practice Tips
Incorporating these techniques into your daily routine could lead to noticeable improvements in physical energy and endurance. Try practicing them in the morning or before physical activity for an added energy boost.
Conclusion: Using Breath to Support Mental Health
Breathing exercises offer a simple, natural way to support mental health by reducing stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms. Through techniques like diaphragmatic breathing, box breathing, and resonant breathing, individuals can activate the parasympathetic nervous system, regulate neurotransmitter levels, and promote a state of calm. The accessible nature of these practices makes them ideal for anyone looking to incorporate a mindful, effective tool into their daily life to support mental well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How often should I practice breathing exercises for mental health?
Daily practice is ideal. Just 5–10 minutes each day can improve stress management and emotional resilience. Consistency helps maximize the mental health benefits.
2. Which breathing technique is best for anxiety?
Box breathing is highly effective for calming anxiety. Its structured rhythm promotes relaxation and focus, making it a go-to method for managing anxious feelings.
3. Can breathing exercises help improve sleep?
Yes, exercises like diaphragmatic and coherent breathing can promote better sleep by calming the nervous system. Practicing them before bed helps prepare your body for rest.
4. What is HRV, and why is it important?
Heart Rate Variability (HRV) measures the variation in time between heartbeats and reflects your body’s stress adaptability. Higher HRV is linked to better emotional resilience and mental health.
5. Are breathing exercises safe for everyone?
Generally, yes. However, intense techniques like fast breathing can cause dizziness. Start slow and consult a healthcare provider if you have respiratory or heart conditions.
6. How quickly will I see results from breathing exercises?
Some people feel immediate relaxation, but consistent practice over a few weeks is needed for lasting mental health benefits like improved HRV and reduced anxiety.
Breatheology Courses
Learn and master conscious breathing through our online breathwork courses. Discover how simple yet powerful breathing techniques can help reduce stress, improve your mental clarity, and boost your physical performance.
Free Breathwork Courses
Kickstart your breath training journey with our free, step-by-step breathing programs designed to help you improve lung capacity, manage stress, and build focus.
Advanced Breathwork Training
Take your breathing mastery to the next level with our advanced breathwork training programs. Build resilience, enhance your endurance, and unlock greater physical and mental performance.
More on Breath and Mental Health
Sources
PubMed Central “The Vagus Nerve’s Role in Regulating Stress and Mood.“
Harvard Health Publishing. “Exercises to relax“
Harvad Business Review “Why Breathing Is So Effective at Reducing Stress“
PubMed Central: Breathwork Interventions for Adults with Clinically Diagnosed Anxiety Disorders
