Meditation & Yoga, Science & Studies
Meditation and Dopamine: Boost Mood, Motivation, and Focus
The interest in meditation has been growing for centuries, transitioning from a spiritual practice to a globally recognized method for maintaining mental and physical health. Recent research uncovers the neurochemical mechanisms underlying meditation’s benefits, particularly its profound effect on dopamine—a key neurotransmitter in the brain’s reward and motivation systems. Understanding this connection provides a glimpse into how meditation rewires the brain for better mood, motivation, and resilience.
What Is Dopamine, and Why Is It So Important?
Among all the main neurotransmitters in the brain, dopamine plays a critical role in signal transmission between nerve cells. It is implicated in several physiological and psychological functions:
- Mood Regulation: Dopamine influences feelings of pleasure and happiness, while low levels have been associated with depression.
- Motivation and Reward: Dopamine reinforces goal-oriented behavior by rewarding actions that help achieve goals.
- Cognitive Functions: Learning, memory, and attention all require optimal levels of dopamine.
- Stress and Resilience: Dopamine increases one’s capacity to adapt to challenges and stress, providing emotional stability.
Disturbances in dopamine levels can lead to a range of issues, including mood disorders and addiction. Meditation emerges as a promising, drug-free method to optimize dopamine functioning and improve overall well-being.
Meditation and Science: The Unfolding Potential of Dopamine
Meditation, once considered primarily a spiritual or mental activity, is now understood to profoundly impact brain chemistry. Studies show that meditation reliably alters dopamine levels, influencing mood, stress response, and cognitive performance. Below are key findings:
Dopamine Release During Meditation
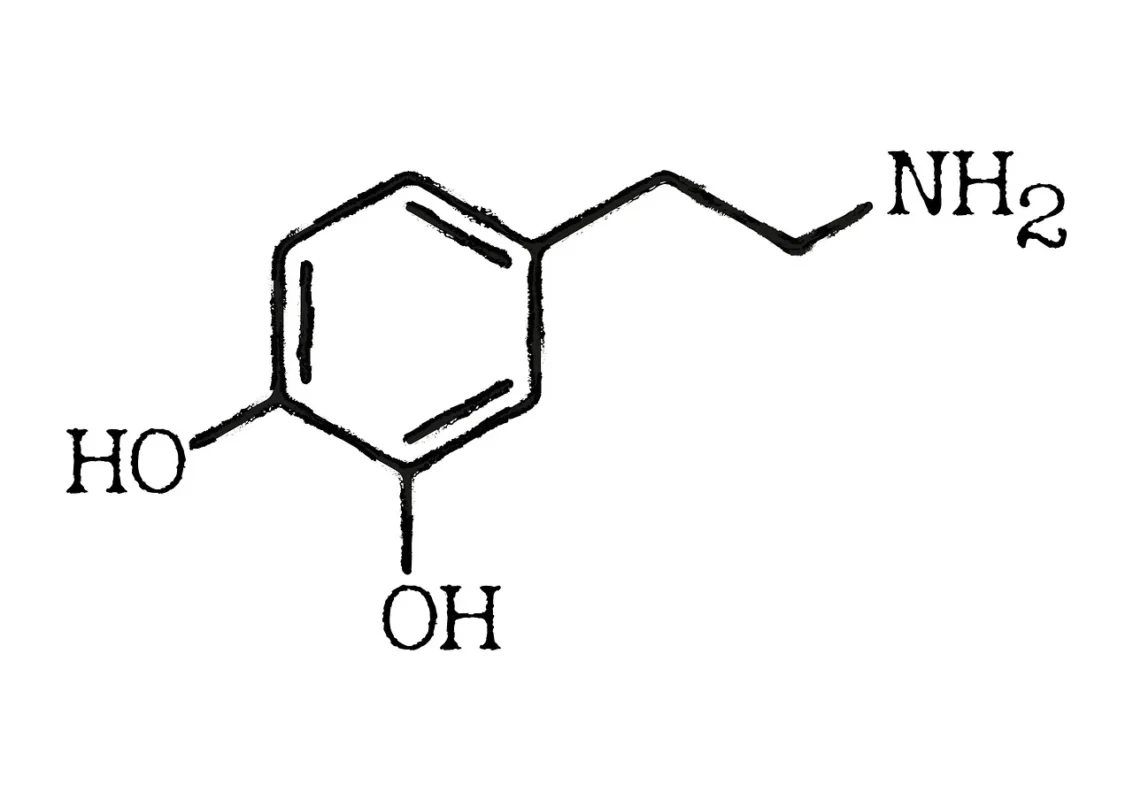
Research has reported significant increases in dopamine levels during meditation. For example, a study using PET imaging showed that during the Yoga Nidra meditation condition, dopamine increased by 65% in the ventral striatum compared to baseline. This increase was associated with heightened relaxation and reduced action-oriented desires (Kjaer et al., 2002).
Stress Reduction via Modulation of Dopamine Levels
Meditation balances catecholamines, including dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine, reducing stress and enhancing emotional stability. Although genetic factors, such as those related to the BDNF and COMT genes, influence individual responses, overall trends indicate reduced stress and stabilized dopamine activity (Jung et al., 2012).
Higher Positive Affect and Emotional Stability
Long-term meditators exhibit higher dopamine levels, associated with positive emotions. Compared to non-meditators, they also show reduced stress markers, further supporting meditation’s role in emotional stability (Jung et al., 2010).
Structural and Functional Brain Changes
Meditation induces structural and functional changes in brain areas responsible for attention, emotional regulation, and self-awareness. These changes are linked to increased dopamine activity and reduced cortisol levels, promoting improved mental health (Esch, 2014).
How Meditation Influences Dopamine Pathways
Meditation affects dopamine production and utilization through several mechanisms:
- Dopamine Increase and Theta Brainwaves
Meditation-induced theta brainwaves are associated with increased dopamine levels, promoting deep relaxation and focused attention. - Cortical-Striatal Connectivity
Dopamine modulates the interaction between the prefrontal cortex and the striatum. Meditation enhances this connectivity, promoting better decision-making and emotional regulation (Kjaer et al., 2002). - Sympathetic Nervous System Regulation
Meditation reduces sympathetic nervous system activity, stabilizing dopamine levels and mitigating the effects of chronic stress (Infante et al., 2001).
Does Meditation Increase Dopamine Receptors?
While research has shown that meditation can increase dopamine levels in the brain, another intriguing aspect to explore is its potential to influence dopamine receptors—the brain’s “locks” that respond to dopamine. These receptors play a vital role in how the brain processes dopamine, affecting motivation, reward, and overall mood.
Dopamine Receptor Density and Brain Plasticity
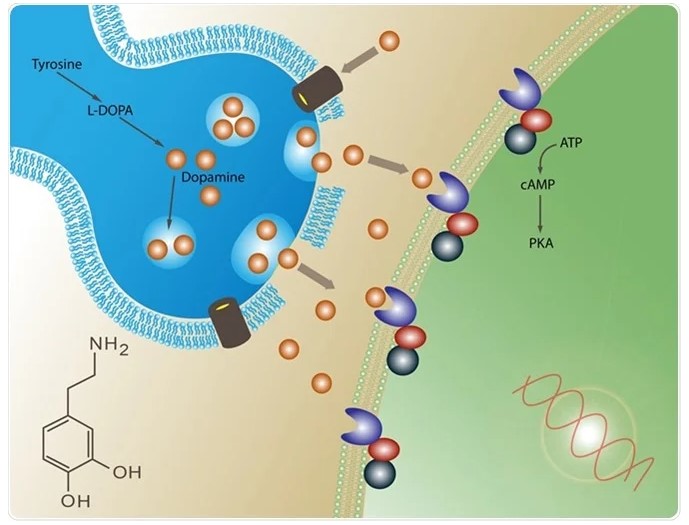
Dopamine receptors are proteins located on the surface of neurons that bind with dopamine to trigger certain neural responses. When we engage in rewarding activities, these receptors activate and reinforce positive behaviors. However, the number and sensitivity of these receptors can vary due to factors such as genetics, environmental influences, and lifestyle choices.
Meditation, as a form of mental training, has been shown to induce neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to reorganize and form new neural connections. Over time, regular meditation practice may lead to increased dopamine receptor density, enhancing the brain’s capacity to respond to dopamine. This increased receptor density is significant because it can improve motivation, focus, and emotional regulation, all of which are essential for maintaining mental well-being.
Research on Meditation and Dopamine Receptors
Some studies have indicated that meditation may not only increase dopamine levels but also affect the brain’s dopaminergic system in a way that improves receptor function. For instance, long-term meditators have shown heightened sensitivity to dopamine, likely due to a greater number of dopamine receptors in the brain regions involved in motivation and emotional regulation.
Additionally, meditation practices that promote mindfulness, such as focused attention and loving-kindness meditation, may specifically impact the areas of the brain responsible for empathy, attention, and emotional processing. As a result, these practices could lead to improved dopamine receptor functionality, which in turn may contribute to better mood regulation, higher motivation, and increased resilience to stress.
How Meditation Enhances Dopamine Receptors
Meditation may improve dopamine receptor sensitivity and density through several mechanisms:
- Stress Reduction: By lowering cortisol levels and reducing stress, meditation allows dopamine receptors to become more responsive. Chronic stress can impair receptor function, so reducing it may help optimize dopamine receptor activity.
- Increased Brain Connectivity: Meditation enhances connectivity between brain regions, such as the prefrontal cortex and the striatum, which are involved in decision-making and reward processing. This enhanced connectivity may promote more effective dopamine receptor activation.
- Neurogenesis and Receptor Growth: Studies suggest that meditation can stimulate the growth of new neurons and dopamine receptors in brain areas related to reward and motivation, such as the ventral striatum. This process, known as neurogenesis, can boost the brain’s ability to respond to dopamine.
Real-Life Benefits of Meditation on Dopamine Levels
The impact of meditation on dopamine translates into several practical benefits:
- Boosting Motivation and Productivity
Elevated dopamine levels enhance focus and drive, making it easier to tackle personal and professional challenges. - Enhancing Emotional Well-Being
Meditation-induced dopamine release improves mood and emotional stability, reducing the risk of anxiety and depression. - Addiction Recovery
Meditation helps restore dopamine balance, reducing cravings and supporting long-term recovery. - Improving Cognitive Performance
Increased dopamine levels enhance learning, memory, and problem-solving abilities. - Promoting Relaxation and Stress Relief
Meditation activates the parasympathetic nervous system, stabilizing dopamine levels and fostering calmness.
How Much Should I Meditate to Enjoy Increased Dopamine?
Here are practical tips for harnessing meditation’s dopamine-boosting benefits:
- Start Small: Begin with 5–10 minutes of meditation daily and gradually increase as you get comfortable.
- Explore Different Practices: Experiment with mindfulness, Yoga Nidra, or transcendental meditation to find what suits you best.
- Be Consistent: Daily practice ensures sustained benefits. Commit to a regular schedule.
- Create a Comfortable Environment: Choose a quiet, distraction-free space for better focus and relaxation.
- Track Progress: Use journaling to monitor improvements in mood, focus, and stress levels.
The Future of Meditation and Dopamine Research
As research on meditation’s effects on dopamine and brain health advances, exciting new possibilities are emerging, including:
- Mental Health Treatment: Complementary use of meditation in therapies for depression, anxiety, and addiction.
- Cognitive Improvement: Enhancing cognitive training programs for aging populations through dopamine optimization.
- Workplace Wellness: Corporate meditation programs to boost employee productivity and resilience.
Conclusion: Meditation as a Powerhouse Booster of Dopamine
Meditation is more than a relaxation technique—it is a deep neurochemical intervention that enhances dopamine activity, improving mental, emotional, and cognitive health. Through regular meditation, individuals can unlock a natural and sustainable pathway to happiness, resilience, and focus.
References
Kjaer et al., 2002 – Increased dopamine release and dopamine receptor density during Yoga Nidra meditation.
Jung et al., 2012 – Meditation’s effect on catecholamines and stress.
Kruis et al., 2016 – The role of meditation in stress and dopamine regulation.
Infante et al., 2001 – Catecholamine levels in transcendental meditation practitioners.
Esch, 2014 – Neurobiology of meditation and mindfulness.
FAQs
What is the fastest way to increase dopamine?
The fastest way to increase dopamine through natural activities are exercising, listening to music, eating dopamine-boosting foods (high-fat, salty, or sugary treats) or achieving small goals. These activities trigger immediate dopamine release, enhancing mood and motivation.
What hormone is released during meditation?
Meditation triggers the release of hormones like dopamine, which enhances focus and mood, and serotonin, promoting relaxation and happiness. It also reduces stress hormones like cortisol, helping to improve emotional balance and overall well-being.
What is the most naturally dopamine-releasing activity?
Highly rewarding and pleasurable activities, such as sex, achieving goals, eating delicious food, or engaging in physical exercise, release significant amounts of dopamine. Among these, sex is one of the most powerful natural triggers for dopamine due to its impact on the brain’s reward system.
What emotion triggers dopamine?
Happiness, excitement, and anticipation are key emotions that trigger dopamine release. Experiencing joy from achieving a goal, engaging in a pleasurable activity, or even imagining a rewarding outcome can activate dopamine pathways, enhancing feelings of motivation and satisfaction.
Breatheology Courses
Learn and master conscious breathing through our online breathwork courses. Discover how simple yet powerful breathing techniques can help reduce stress, improve your mental clarity, and boost your physical performance.
Free Breathwork Courses
Kickstart your breath training journey with our free, step-by-step breathing programs designed to help you improve lung capacity, manage stress, and build focus.
Advanced Breathwork Training
Take your breathing mastery to the next level with our advanced breathwork training programs. Build resilience, enhance your endurance, and unlock greater physical and mental performance.
Relevant Links:
- How to Increase Gamma Brain Waves
Discover how gamma brain waves enhance focus, creativity, and motivation, supporting mental clarity through meditation. - How Breathing Affects Mental Health
Explore the connection between breathing techniques and improved mental health, reducing stress and boosting mood naturally. - How Proper Breathing Can Decrease Stress and Anxiety
Learn how intentional breathing can alleviate stress and anxiety, enhancing overall well-being and focus. - Breathwork for Depression
Understand how breathwork techniques can help combat depression and enhance dopamine production for a positive mindset. - Neurotransmitters and Breathing
Dive into the science of how breathing impacts neurotransmitters like dopamine, serotonin, and endorphins to elevate your mood.